
The content in this article is for general information and unearned revenues are amounts received in advance from customers for future products or services. education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- Auditors play a critical role in verifying that unearned revenue is accounted for correctly.
- Recognizing unearned revenue as a liability helps maintain the integrity of financial reporting and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
- Best practices include maintaining detailed records, regularly reviewing and adjusting entries, and ensuring compliance with relevant accounting principles and standards.
- Unearned revenue, also known as prepaid revenue or deferred revenue, is a fundamental concept in accounting.
- This changes if advance payments are made for services or goods due to be provided 12 months or more after the payment date.
- When a company pays money in advance to another service provider, it will have to receive the services in the future.
How to record unearned revenue?
This avoids overstatement of income and ensures accurate timing of revenue recognition. For instance, if a customer prepays $600 for a 12-month subscription, the company lists this amount as unearned revenue on the balance sheet and recognizes $50 as revenue each month. It is classified as a liability because the company has an obligation to deliver goods or services in the future.

Income Method
When a company receives advance payments from customers, it records these payments as a liability rather than revenue. This is because the company has not yet fulfilled its obligation to deliver the goods or services. Recognizing unearned revenue as a liability helps maintain the integrity of financial reporting and ensures compliance with accounting standards. Recording unearned revenue involves debiting the cash account and crediting the unearned revenue account. As the company fulfills its obligations by delivering goods or services, the unearned revenue is gradually recognized as earned balance sheet revenue.
- Common challenges include accurately tracking the timing of revenue recognition, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, and managing customer expectations.
- Investors and creditors often scrutinize a company’s financial statements when making decisions.
- Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article.
- Once the unearned income is classified, the next step is to record the transaction in the company’s financial records.
- Under this method, the unearned revenue is recognized as income at the time of receipt rather than being recorded as a liability.
Unearned Revenues Vs. Prepaid Expenses – Key Different Explained
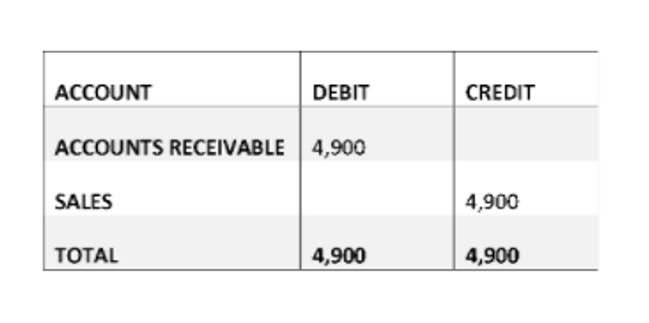
Recognizing revenue only when earned presents a truthful view of a company’s financial position, which is crucial for internal analysis and external reporting. Accurately handling unearned revenue accounting maintains transparency and helps prevent the overstatement of profits. It also adheres to the matching principle, aligning revenue with the period in which services are provided. When the company receives advance payment, it debits cash and credits unearned revenue. In accounting and finance, unearned revenues are typically classified as liabilities until the related services are performed or products delivered. Under GAAP, unearned revenue must be recorded as a liability and recognized as revenue when the related goods or services are delivered or performed.

Company

The company’s financial statements reflect the timing of income recognition, which is defined by the matching principle in accounting. This means that expenses should be matched with the revenue they help generate to provide a clearer look at financial performance. In the construction industry, projects are often long-term and payments are received at various stages of completion. Here, it is crucial to match revenue recognition with the progress of the project, often using a percentage-of-completion method. This approach helps in accurately reflecting the financial performance and obligations of the company over the duration of the project.
It represents money received from customers for goods or services that have not yet been delivered https://www.bookstime.com/articles/contribution-margin-ratio or performed. As such, it constitutes an obligation for the company to provide these goods or services in the future. Until the company fulfills this obligation, the amount is recorded as a liability. Once the service or product is delivered, the liability is removed, and the payment is recognized as revenue. Certain industries have unique considerations when it comes to unearned revenue and the treatment of advance customer payments.

This reflects receiving cash that the company is obligated to earn by delivering those goods or services. It is treated as a liability because the revenue has still not been earned and represents products or services owed to a customer. As the prepaid service or product is gradually delivered over time, it is recognized as revenue on the income statement. These accrual accounting standards require future revenue to be recognized when earned, not received. Unearned revenue, also known as prepaid revenue or deferred revenue, is a fundamental concept in accounting. It represents the funds a company receives in advance for goods or services it is yet to deliver or perform.
Accounting for Unearned Revenue
These are payments made in advance to receive products or services at a later date. Below, we’ll walk through how to record unearned revenue, how unearned revenue impacts financial statements and balance sheets, and examples of unearned revenue. Note that when the delivery of goods or services is complete, the revenue recognized previously as a liability is recorded as revenue (i.e., the unearned revenue is then earned). Failure to record unearned revenue correctly can lead to cash flow misjudgments and budgeting errors. It can also affect tax liabilities, potentially resulting in penalties or inaccurate filings.
